Study Cloud and AI in Metro College of Technology
Learn hands-on AI integration using top cloud platforms. Join one of Canada’s fastest-growing sectors for tech
professionals.
Learn About Metro College
Study Cloud and AI in Metro College of Technology
Learn hands-on AI integration using top cloud platforms. Join one of Canada’s fastest-growing sectors for tech
professionals.
Learn About Metro College
Study Cloud and AI in Metro College of Technology
Learn hands-on AI integration using top cloud platforms. Join one of Canada’s fastest-growing sectors for tech
professionals.
Learn About Metro College
Study Cloud and AI in Metro College of Technology
Learn hands-on AI integration using top cloud platforms. Join one of Canada’s fastest-growing sectors for tech
professionals.
Learn About Metro College
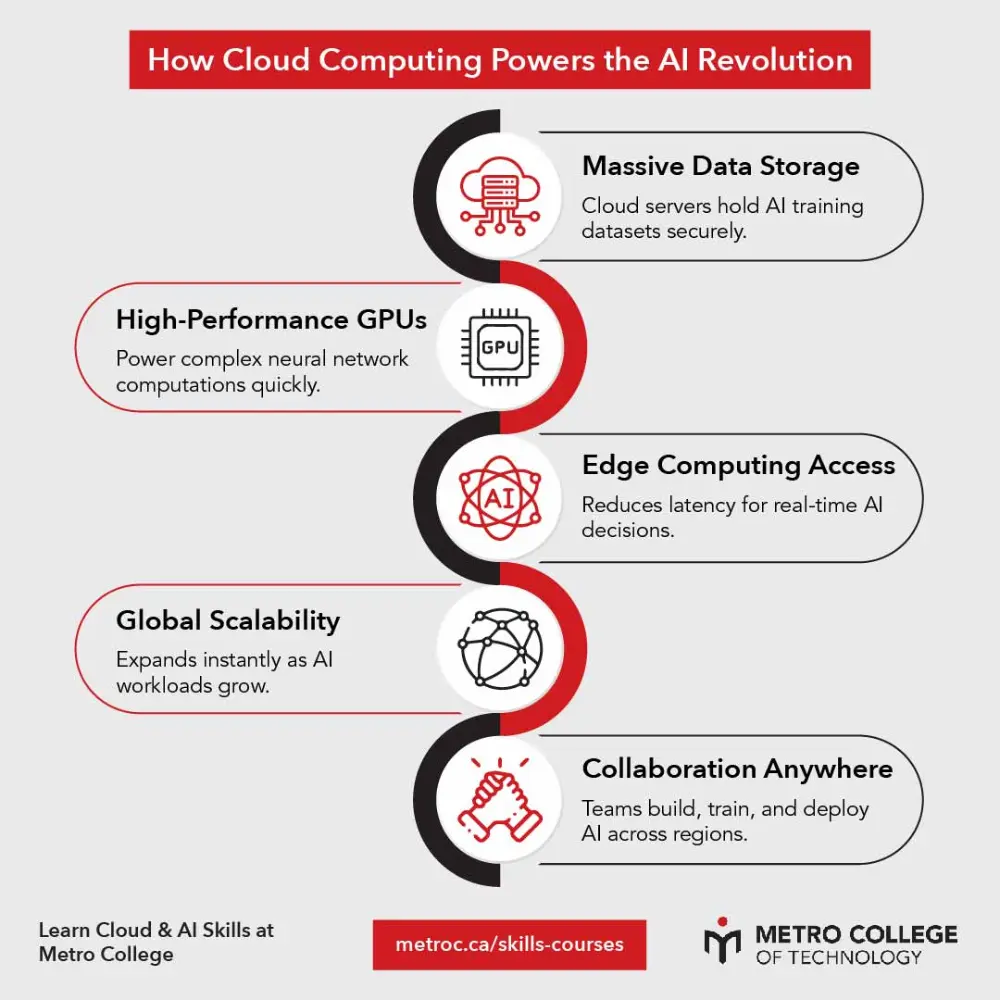
Cloud computing powers nearly every modern AI innovation, from language models and smart assistants to autonomous
vehicles and global data networks. It provides the storage, scalability, and computing strength that artificial
intelligence requires to process enormous datasets efficiently. Without cloud infrastructure, AI systems would
struggle to train, deploy, and learn in real time. This article explores how cloud technology drives the AI
revolution, the key systems that make it work, and how aspiring professionals can prepare for careers in this
fast-growing industry.
Key Takeaways:
- Cloud computing supports AI development by delivering powerful, scalable resources for data processing and machine
learning.
- Emerging technologies like edge computing, GPUs, and virtualization make AI faster and more efficient.
- Professionals trained in cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are in high demand across global
industries.
What Is Cloud Computing and How It Works
Cloud computing
delivers IT services, including servers, databases, networking, and analytics, over the internet. Instead of
buying and maintaining physical hardware, businesses rent computing power from cloud providers. This model allows
organizations to scale quickly, pay only for what they use, and innovate faster.
At its core, cloud computing operates through data centers filled with virtualized servers. Each server is capable of
running multiple applications simultaneously, using virtualization to allocate resources dynamically. These servers
are managed remotely, meaning developers and businesses can access immense computing power from anywhere in the world.
Cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) dominate the market.
They offer pre-built tools for machine learning, AI model deployment, and big data analytics. Students studying cloud
computing gain hands-on experience with these systems, preparing them to meet the growing demand for cloud architects,
DevOps engineers, and AI specialists in Canada’s tech sector.
Key Technologies Behind Cloud: Edge Computing, GPUs, and Virtualization
Cloud computing relies on a combination of advanced technologies that make modern AI possible. These systems ensure
that data processing happens faster, more securely, and closer to where it’s needed most.
Edge Computing
Edge computing moves data processing closer to the user, reducing latency and improving speed. Instead of sending
every piece of information back to centralized servers, edge devices like routers or local nodes handle preliminary
computations. This reduces data congestion and enables real-time AI applications such as smart traffic systems or IoT
sensors in healthcare.
GPUs (Graphics Processing Units)
GPUs accelerate the heavy computations used in AI model training. Each GPU contains thousands of cores that process
tasks simultaneously, drastically cutting down training time for neural networks. As AI models become more complex,
GPUs have replaced traditional CPUs in most large-scale machine learning operations.
Virtualization
Virtualization divides physical servers into multiple virtual machines, each running its own operating system. This
technology maximizes resource efficiency and allows multiple users to share the same physical hardware securely.
It’s the foundation of every cloud infrastructure, providing flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency.
Containerization
Containerization packages applications and their dependencies into lightweight, portable containers. Tools like
Docker and Kubernetes ensure consistent performance across different computing environments. This approach simplifies
AI model deployment and makes scaling easier across hybrid and multi-cloud setups.
The Role of Cloud in Enhancing AI and Machine Learning Applications
Cloud computing enables AI models to process massive datasets, train faster, and deploy globally. Machine learning
systems rely on vast computing power and data storage that only cloud platforms can deliver. As organizations digitize
operations, AI workloads increasingly move to the cloud for cost efficiency and agility.
Cloud platforms also provide Machine
Learning-as-a-Service (MLaaS) offerings. These ready-to-use frameworks allow businesses to build, test, and
deploy AI models without investing in expensive infrastructure. Services like AWS SageMaker and Azure Machine Learning
simplify the process for developers while improving collaboration across global teams.
For students, cloud-based AI tools offer learning opportunities that bridge theory and real-world application.
Building predictive models, processing data with TensorFlow on the cloud, or deploying chatbots through Azure prepares
graduates for high-demand careers in AI-driven industries like finance, healthcare, and logistics.
Study Cloud and AI in Metro College of Technology
Learn hands-on AI integration using top cloud platforms. Join one of Canada’s fastest-growing
sectors for tech professionals.
Learn About Metro College
How Cloud Enables Real-Time Data Processing and Smarter Insights
Speed is everything in the world of artificial intelligence. Cloud computing delivers the infrastructure that makes
real-time data processing possible. Instead of relying on limited local servers, organizations use distributed cloud
networks to analyze, store, and act on information the moment it’s generated. The result is smarter
decision-making, faster automation, and stronger customer experiences.
Modern businesses operate in milliseconds. Financial institutions react to market fluctuations instantly. Retailers
adjust pricing based on live demand. Logistics companies track shipments across continents without interruption. Cloud
systems power this agility by combining global networks, caching layers, and AI frameworks that process billions of
data points simultaneously. Real-time analytics no longer belong to tech giants alone; they’re accessible to any
organization connected to the cloud.
Distributed Processing
Distributed processing spreads computational workloads across multiple cloud servers operating in different regions.
Instead of sending data to a single machine, parallel computing breaks it into smaller chunks processed
simultaneously. This design ensures near-zero latency for critical applications like fraud detection, autonomous
vehicles, and real-time translation systems. When one node experiences high traffic, others immediately absorb the
load, keeping performance seamless worldwide. For AI professionals, understanding distributed architecture is key to
designing systems that scale with demand without slowing down.
Stream Analytics
Stream analytics turns continuous data into actionable intelligence. Cloud-based systems like Azure Stream Analytics
and Amazon Kinesis capture information from sensors, apps, and social feeds in real time. This enables businesses to
detect patterns and respond instantly, for instance, alerting a hospital when a patient’s vital signs change, or
adjusting energy output in a smart grid. The ability to analyze data streams on the fly transforms how organizations
make decisions. Instead of reacting to problems after they happen, they anticipate them before they occur.
In-Memory Computing
Traditional databases store and retrieve data from disk drives, creating bottlenecks when processing large datasets.
In-memory computing eliminates this delay by keeping information in RAM, allowing data to be accessed almost
instantly. This approach dramatically improves the speed of recommendation engines, AI chatbots, and financial
forecasting systems. Cloud providers combine in-memory frameworks with auto-scaling capabilities so performance
remains consistent even during data surges. For students entering the analytics field, mastering in-memory frameworks
like Apache Ignite or SAP HANA opens pathways to roles focused on real-time computing efficiency.
Predictive Intelligence
The combination of AI and cloud analytics gives rise to predictive intelligence, the ability to forecast what happens
next. Predictive models running on cloud platforms analyze both historical and real-time inputs to make accurate
projections. Banks use these models to detect potential credit card fraud, e-commerce companies use them to anticipate
buying trends, and factories use them to schedule maintenance before equipment breaks down. Because these systems
learn continuously, their accuracy improves with every new dataset processed.
For professionals entering the workforce, this shift represents opportunity. The demand for specialists who can
design predictive systems using cloud computing continues to grow across finance, healthcare, and logistics.
Understanding how to connect live data streams, model outcomes, and deliver insights in real time is one of the most
valuable skills in the AI-driven economy.
Cloud Applications in Media, Gaming, Retail, and Industrial AI Use Cases
Cloud computing drives innovation across every major sector, from entertainment and retail to industrial operations.
Its scalability, speed, and accessibility have made it the backbone of digital transformation worldwide. By enabling
instant access to high-performance computing, businesses can run complex algorithms, automate workflows, and manage
global operations without investing in expensive hardware. For students and professionals pursuing cloud careers,
these sectors demonstrate how real-world industries harness data, AI, and the cloud to create smarter systems and
better user experiences.
Media and Entertainment
The media industry depends on the cloud to deliver personalized, high-quality content at scale. Those who specialize
in digital media marketing and analysis are
responsible for identifying trends using AI algorithms. Streaming platforms host massive libraries of shows, music,
and films in the cloud, where AI algorithms analyze audience behaviour in real time. Every pause, replay, and search
contributes to a growing dataset that fuels recommendation engines. These systems use machine learning to predict what
a viewer wants to watch next, sometimes before they even realize it themselves.
Behind the scenes, production studios also benefit. Cloud-based rendering allows editors and animators to collaborate
across continents, reducing time and cost in post-production. Services like AWS Elemental Media and Google Cloud Video
Intelligence process high-definition footage seamlessly, enabling faster workflows for global media companies. For
aspiring professionals, understanding how cloud computing powers streaming, editing, and analytics opens opportunities
in content delivery, digital marketing, and data engineering.
Gaming
Cloud computing has revolutionized the gaming industry. Once limited by local hardware, developers now use the cloud
to design immersive, multiplayer experiences accessible from virtually any device. Platforms like AWS GameLift, Google
Cloud for Games, and Microsoft Azure PlayFab handle the heavy lifting, real-time rendering, data synchronization, and
AI-driven environment control.
Artificial intelligence hosted on the cloud also enhances gameplay. Machine learning models adjust difficulty levels
dynamically, customize challenges for players, and detect cheating behaviours. Gamers enjoy smoother experiences with
reduced lag because cloud servers are distributed across multiple regions. The result is responsive, data-rich
environments where developers can focus on creativity instead of infrastructure.
For students, this field bridges cloud architecture with real-time AI deployment. Careers in game development, data
analytics, and cloud architecture now merge creativity with technology, skills highly sought after by studios and
publishers.
Retail and E-Commerce
In retail, cloud computing has become a strategic engine for personalization and customer insight. Every online
interaction generates valuable data, clicks, searches, purchases, and reviews that cloud analytics platforms process
in real time. AI tools interpret this data to predict demand, recommend products, and automate marketing campaigns
tailored to each shopper.
For example, retailers use predictive models to forecast which products will trend during holidays or sales events.
Inventory systems automatically adjust stock levels, reducing waste and maximizing profit. Cloud-powered CRM tools
integrate across websites, apps, and stores to maintain consistent customer experiences.
Major global brands such as Walmart and Shopify rely on AI cloud solutions to operate their vast supply chains efficiently. For students
studying business analytics or e-commerce, learning how to connect AI models with cloud systems can lead to roles in
data strategy, retail analytics, and customer experience management.
Industrial AI
Manufacturing, logistics, and energy companies depend on cloud infrastructure to analyze real-time data from
thousands of sensors and connected devices. Every machine, conveyor belt, and vehicle generates continuous streams of
information. Cloud-based AI systems process these inputs instantly to detect inefficiencies or maintenance needs
before they disrupt production.
Predictive maintenance, powered by the cloud, reduces costly downtime. Sensors embedded in machines send performance
data to cloud analytics engines, which forecast potential failures and schedule repairs proactively. In logistics, AI
algorithms optimize delivery routes and warehouse operations, cutting fuel consumption and improving speed.
Industries like aerospace, automotive, and energy also rely on digital twins, virtual replicas of physical systems
stored in the cloud. These models simulate operations, test changes safely, and guide engineering decisions with
data-driven accuracy. For future professionals, expertise in cloud-driven industrial analytics opens doors to
high-demand roles in IoT management, operations intelligence, and smart manufacturing systems.
Benefits of Cloud Computing: Scalability, Low Latency, and Cost-Effectiveness
The cloud’s biggest advantage lies in its ability to scale and adapt instantly to business needs. Organizations
only pay for what they use, allowing smarter budgeting and resource management.
- Scalability: Instantly expand or reduce computing resources based on demand without hardware
investment.
- Low Latency: Distributed data centers bring computation closer to users, improving speed and
reliability.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The pay-as-you-go model removes upfront capital costs, making advanced AI
accessible to startups and large enterprises alike.
- Security and Compliance: Cloud providers offer encryption, compliance frameworks, and 24/7
monitoring to protect sensitive information.
For students, understanding these benefits helps bridge the gap between technical learning and business strategy.
Cloud training equips you to design infrastructure that aligns with both efficiency and innovation goals.
Challenges and Solutions in Deploying Cloud Infrastructure Worldwide
Global cloud adoption continues to grow rapidly, yet it faces several technical and regulatory hurdles. These
challenges vary from region to region, depending on connectivity, compliance laws, and infrastructure maturity.
Data Privacy and Compliance
International cloud deployments must comply with local regulations such as GDPR or Canada’s PIPEDA. Cloud
professionals ensure data sovereignty by configuring secure storage regions and encryption standards.
Network Reliability
Latency and downtime can disrupt global operations. Solutions include using Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and
multi-region redundancy to maintain continuous service.
Cybersecurity Threats
Cloud systems are prime targets for cyberattacks. Advanced authentication, threat intelligence, and continuous
monitoring mitigate these risks effectively.
Skills Gap
The shortage of qualified cloud engineers and AI specialists limits growth. Educational programs like those at Metro
College prepare students with practical, hands-on training in cloud infrastructure and data systems.
FAQ
1. Why is cloud computing crucial for AI development?
AI systems need vast computational power and data storage. Cloud platforms provide scalable resources that enable AI
training, model deployment, and continuous learning efficiently.
2. Which cloud certifications help with career growth?
Certifications from AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud validate your technical expertise and open doors to roles like cloud
architect, data engineer, and AI specialist.
3. What career opportunities are available in cloud computing and AI?
Graduates can work as cloud engineers, AI developers, data architects, or machine learning engineers. These
roles are in high demand across industries like finance, healthcare, and technology, where organizations rely on
cloud-based AI solutions to improve efficiency, scalability, and innovation.
The Impact of Cloud Computing on Global AI Adoption and Innovation
Cloud computing continues to accelerate AI development, fueling breakthroughs across every industry. It allows
researchers, startups, and global enterprises to collaborate at an unprecedented scale. For students and
professionals, mastering cloud technology means participating in one of the most influential shifts in modern
computing. The AI revolution thrives on the cloud, and the next generation of innovators, trained in cloud computing,
will define its future impact on global progress.
Build Your Career in Cloud Computing
Learn AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud skills that power today’s AI revolution. Gain practical
training for roles shaping the future of technology.
Explore Skill-Based Courses